Nuclear Reactions
Nuclear Reactions: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Nuclear Reaction, Q-value of a Nuclear Reaction, Exoergic Nuclear Reactions, Endoergic Nuclear Reactions, Conservation Laws in Nuclear Reactions, Nuclear Energy, Q-Value in Alpha Decay Reactions, etc.
Important Questions on Nuclear Reactions
Thermal neutrons at the room temperature have an energy of Half-life of neutrons is minutes. If a source gives out a beam of neutrons, at what distance from the source, half the neutrons would have decayed?
The average translational kinetic energy depends only on _____ temperature.
Does average kinetic energy depend only on temperature?
How do you find the kinetic energy of a thermal neutron?
What is the average kinetic energy of a molecule in terms of temperature?
In the following nuclear reaction stands for
When nuclei are bombarded by protons, the resultant nuclei is . The emitted particles will be
What is the nuclear equation for the electron capture decay of ? Calculate the energy released.
The complete reaction equation for electron capture by is . Calculate the energy released in .
Write the complete reaction equation for electron capture by . Calculate the energy released.
In beta decay, the typical Q value is approximately:
The nucleus of element undergoes −decay. If -value of the reaction is , then the kinetic energy of −particle is:
Consider the following nuclear reactions:
I.
II.
Then,
A nucleus of mass number and atomic number , after many disintegrations of and radiation, decays into other nuclei whose mass number is and atomic number is The numbers of and radiations will be:
Identify the missing product in the given nuclear reaction
A nuclear reaction is represented by the following equation: . This reaction is an example of
Consider the nuclear fission reaction using the graph given answer the following question.
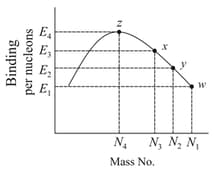
What is the -Value of the reaction?
The threshold energy for the following nuclear reaction to proceed is
atomic mass of is
atomic mass of is
atomic mass of is
atomic mass of is
A free neutron decays to a proton but a free proton does not decay to a neutron. This is because
